排序链表
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
示例 1:
1
2
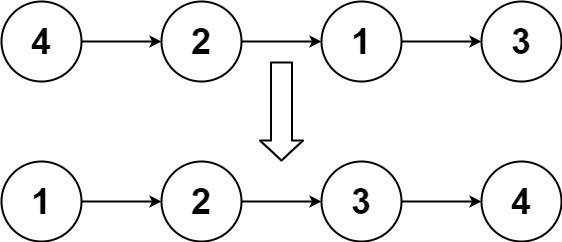
| 输入:head = [4,2,1,3]
输出:[1,2,3,4]
|
示例 2:

1
2
| 输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
|
示例 3:
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 5 * 104] 内
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
进阶:你可以在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序吗?
方法一,递归写法归并排序,空间复杂度logn
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode mid = findMid(head);
head = sortList(head);
mid = sortList(mid);
return merge(head, mid);
}
private ListNode findMid(ListNode node) {
ListNode fast = node;
ListNode slow = node;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode mid = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
return mid;
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode h = new ListNode(0);
ListNode tail = h;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
tail.next = list1;
tail = tail.next;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
tail.next = list2;
tail = tail.next;
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
tail.next = list1 != null ? list1 : list2;
return h.next;
}
}
|

