链表相交(相交链表)
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
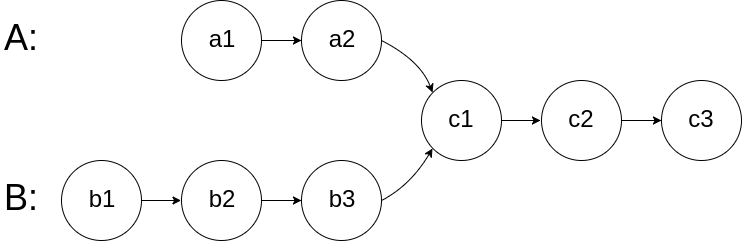
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
示例 1:

1
2
3
4
5
| 输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at '8'
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
|
求出两个链表的长度之差,长的一条移动到和短的一条同样的位置,遍历整条链表并比较是否相等
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int la = 0,lb=0;
ListNode a = headA;
ListNode b = headB;
while(a!=null){
la++;
a=a.next;
}
while(b!=null){
lb++;
b=b.next;
}
if(la>=lb){
for(int i=0;i<la-lb;i++){
headA=headA.next;
}
}
else{
for(int i=0;i<lb-la;i++){
headB=headB.next;
}
}
while(headA!=null&&headB!=null){
if(headA==headB){
return headA;
}
headA=headA.next;
headB=headB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
|
假设链表A相交前的长度是a,链表B相交前的长度是b,公共长度是c
i从a1出发走到头后再从b1出发,走到交点时走过的路程是a+c+b
j从b1出发走到头后再从a1出发,走到交点时走过的路程是b+c+a
走过的路程相等,也就是两个指针会在交点相遇,如果没有交点,那么c=0,两个指针会在null相遇
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode a = headA;
ListNode b = headB;
while (a != b) {
a = a == null ? headB : a.next;
b = b == null ? headA : b.next;
}
return a;
}
}
|

